News
Article in Liquid Crystals Reviews
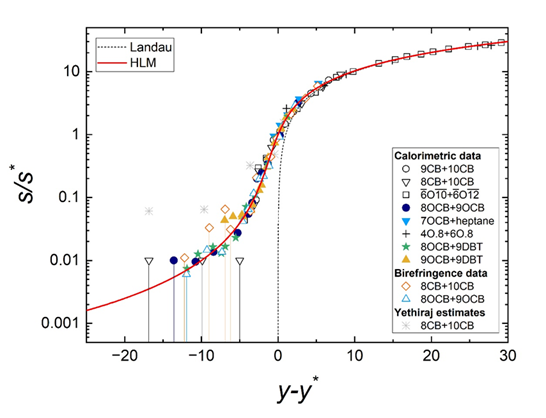
George Cordoyiannis, in collaboration with J. Thoen and C. Glorieux (KU Leuven, Belgium), P. Losada-Pérez (Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium), I. Lelidis (University of Athens, Greece), and C.S.P. Tripathi (Banaras Hindu University, India), has published a review article entitled “The Halperin-Lubensky-Ma argument on the nature of the liquid-crystalline nematic-to-smectic A phase transition: what we have learnt from experiments over the past 50 years” in Liquid Crystals Reviews. This article comprehensively reviews half century of experiments that aimed to detect the fluctuation-induced weakly-first-order character of the nematic-to-smectic A (N-SmA) phase transition in liquid crystals, based on the Halperin-Lubensky-Ma (HLM) argument. High-resolution calorimetric and optical birefringence studies, including some conducted by the authors of this work, exhibit remarkable scaling consistent with the HLM predictions. This experimental demonstration of HLM in liquid crystals is of major importance for a wide range of physical systems, from superconductors to quantum chromodynamics, in which fluctuation-induced first-order transitions occur.
https://doi.org/10.1080/21680396.2025.2602170
Review article on Tomonaga-Luttinger liquids
The journal Nature Reviews Physics has published a review article entitled “Platforms for the realization and characterization of Tomonaga–Luttinger liquids”. In the article, a colleague from the department, Martin Klanjšek, together with an international group of collaborators, provides an overview of the field of physics that has developed over the past two decades based on the theoretical concept of the Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid. The concept describes the physics of interacting quantum particles in one dimension, where, compared to the more common case of three dimensions, the role of interactions is so strong that it leads to very unusual collective behavior, which is, however, entirely universal, applying equally to fermions, bosons, and anyons. The article demonstrates how this concept has proven successful in describing experimental results in such diverse systems as organic conductors, carbon nanotubes, quantum wires, topological edge states in quantum spin Hall insulators, Josephson junctions, Bose liquids in nanocapillaries, and quantum spin chains and ladders.
Link to the article: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42254-025-00866-w
Article in Advanced Materials
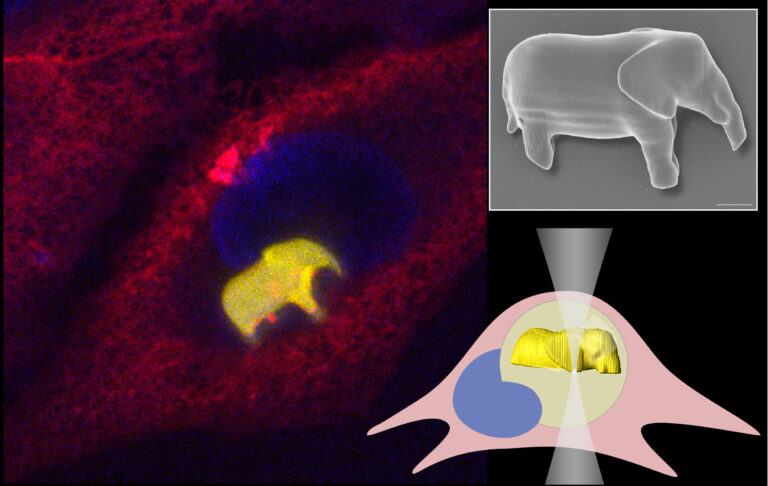
Researchers Maruša Mur, Aljaž Kavčič, Uroš Jagodič, Rok Podlipec and Matjaž Humar from Condensed Matter Physics Department of the Jožef Stefan Institute have shown that 3D printing can be performed inside a living human cell. First, they injected droplets of a bio-compatible photo-curable material into cells. Then, using a highly focused laser beam, they selectively illuminated the printing material and polymerized it. By moving the laser beam in three dimensions, it is possible to “draw” complex structures of any shape with sub-micrometer resolution. Using this method, the team printed various structures, from geometric patterns to microlasers and even small elephants, all inside living human cells. The cells containing such structures can migrate and undergo cell division where the structure is passed into one of the daughter cells. By transforming living cells into miniature environments for 3D printing, this work pushes the boundaries of what is possible at the intersection of biology, physics, and engineering, offering a powerful new tool for exploring the workings of life from the inside out. The results were published in a paper in Advanced Materials, that was selected as an Editor’s Choice Paper.
The article was published in the journal Advanced Materials. M. Mur, A. Kavčič, U.… Read the rest “Article in Advanced Materials”
Biophotonics of lipid droplets: from natural optical resonators to highly precise sensors of dynamic processes in adipocytes
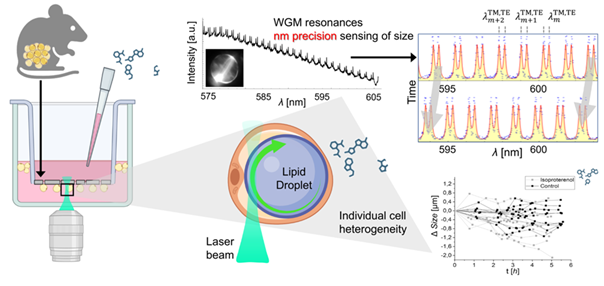
Colleagues from the department, Rok Podlipec, Ana Krišelj, and Matjaž Humar, in collaboration with the Department of Biochemistry, Molecular and Structural Biology and colleagues from the Helmholtz Center in Munich, have published an article in ACS Sensors on an exceptionally precise method for studying rapid dynamic processes at the level of individual adipocytes. In the study, they employed laser‑excited so‑called “whispering gallery mode” (WGM) optical resonances in lipid droplets of live primary adipocytes, achieving nanometer‑scale accuracy in measuring droplet size, which significantly surpasses the resolution of conventional microscopy. By monitoring their dynamics, they explored complex responses to pharmacological agents, variability among individual cells—undetectable with standard bulk assays—and early changes in cell viability, faster than conventional tests. The presented method paves the way for investigations of metabolism and obesity‑related diseases at the level of single adipocytes and tissues.
More information can be found here: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssensors.5c03272
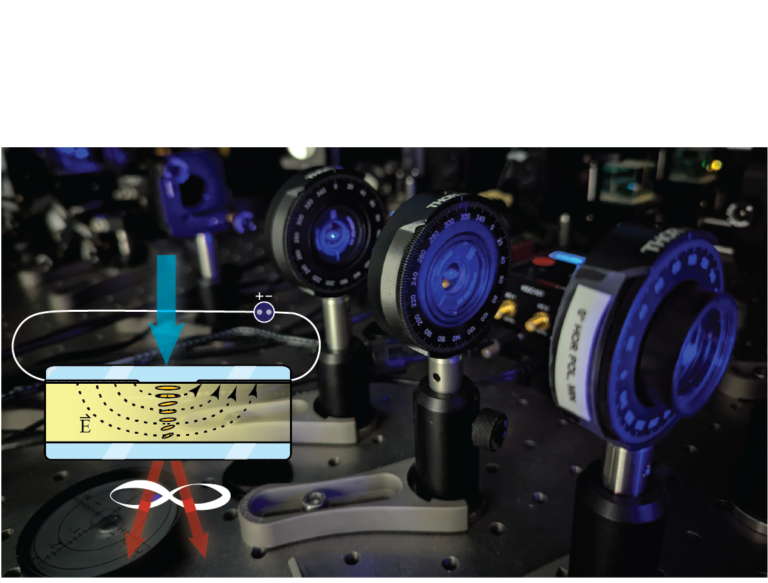
Electrically and Geometrically Tunable Photon Pair Entanglement from Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystal
Entangled photons represent one of the key building blocks of modern quantum technologies. In our study Electrically and Geometrically Tunable Photon Pair Entanglement from Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystal, published in Advanced Science, we demonstrated that quantumly entangled photon pairs can be generated in ferroelectric nematic liquid crystals (FNLCs), while simultaneously enabling continuous tuning of their degree of entanglement.
We showed that the thickness of the liquid crystal sample, in combination with the molecular twist, has a significant impact on the quantum state of the photons generated via spontaneous parametric down-conversion. By appropriately varying these two parameters, it is possible to transition from separable to fully entangled states (within the limits of experimental uncertainty). Furthermore, we demonstrated that the degree of entanglement can be dynamically controlled in real time using an external electric field, which influences the molecular orientation within the sample.
The ability to achieve fast and straightforward electrical control over molecular orientation—and consequently over the quantum state—constitutes a key advantage of liquid crystals compared to conventional solid-state nonlinear crystals. These results point toward the development of so-called “quantum displays,” in which each pixel would function as an independent, electronically controlled quantum light source.
S. Klopčič, A. Kavčič, N. Sebastián, and M.… Read the rest “Electrically and Geometrically Tunable Photon Pair Entanglement from Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystal”
