News
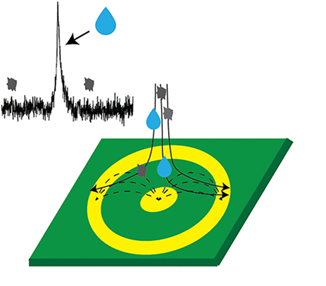
The First Selective Detection of Respiratory Droplets in Air
The transmission of infectious diseases via aerosols in the indoor air remains a major public health hazard. Infected people expel respiratory droplets through breathing, coughing and sneezing, which can remain airborne for hours and contribute to the spread of infections.
Researchers Matjaž Malok, Darko Kavšek and Prof. Maja Remškar from the Department of Condensed Matter Physics at The Jožef Stefan Institute have developed the first sensor based on an innovative method for detecting individual respiratory droplets in the air. The detection is selective without the influence of other air pollutants, unlike existing air quality meters that do not separate respiratory droplets from solid particles. The selectivity of the detection is based on the difference in dielectric constant between water and solid particles.
In addition to respiratory droplets, the sensor device is suitable for measuring particles with a high dielectric constant, such as TiO2, droplets of cooling lubricants in the metal industry and pollen in outdoor air. The use of these devices enables data-driven ventilation, energy savings, and highlights the need for infection prevention measures in hospitals, schools, gyms, and other public spaces.
The article is published in the journal ACS Sensors, https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.5c02057

Magnetic resonance imaging using a straight wire magnetic field for spatial signal encoding : imaging verification with 2D experiments and 3D modeling
Spatial encoding in MRI is usually performed using gradient coils that produce a linearly increasing magnetic field Bz in a desired spatial direction such that its gradient is constant. However, it has been shown that spatial encoding in MRI can also be performed with coils that produce nonlinear magnetic fields. In this study, the performance of different types of nonlinear encoding coils, which have a simple design based on the use of a straight wire segment as a building block and a source of a highly nonlinear magnetic field, was experimentally tested in 2D and by simulation in 3D on coils with a nonsymmetric and a symmetric arrangement of these wire segments. All images were reconstructed using our new reconstruction method, in which the signals spatially encoded by nonlinear coils are first transformed from the time- to the frequency-domain, yielding a distorted image (spectrum), which is then geometrically and intensity corrected. The results of the study may help advance the design of “gradient” coils towards freer geometries, higher magnetic field gradients or lower inductance and thus faster imaging.
TUŠAR, Kaja, SERŠA, Igor. Magnetic resonance imaging using a straight wire magnetic field for spatial signal encoding : imaging verification with 2D experiments and 3D modeling.… Read the rest “Magnetic resonance imaging using a straight wire magnetic field for spatial signal encoding : imaging verification with 2D experiments and 3D modeling”
Tailoring polysaccharide-based aerogels for potential food applications: Structural and hydration characterization by NMR relaxometry and diffusometry
Polysaccharide-based aerogels are promising candidates for food-related applications due to their high surface area, adjustable porosity, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. We investigated chitosan, sodium alginate, and xanthan gum aerogels. Each polysaccharide exhibited unique structural and physicochemical behavior depending on polymer concentration, which influenced the final aerogel properties such as bulk density, pore size, surface area, and water absorption. NMR relaxometry and diffusometry were employed for a detailed characterization of pore structure, hydration behavior, and molecular mobility.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0141813025092542)

Multimodal analysis of whole slide images in colorectal cancer
Multimodal models are becoming increasingly prominent in various areas of medicine, as they allow for fusion of different types of data, such as histopathological images, clinical data, and biomarkers. We analyzed how these approaches can enhance diagnostic accuracy, survival prediction, or treatment response, in colorectal cancer using whole slide images and other modalities. We also discuss the challenges in using these technologies.
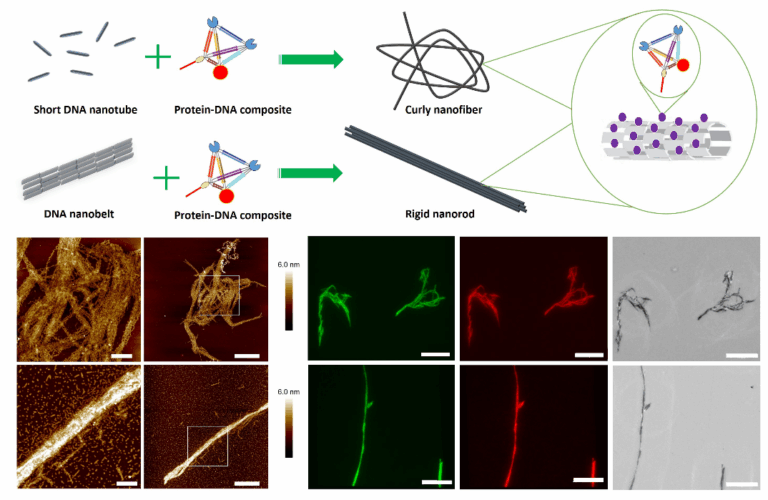
Article in Small
Miha Škarabot participated in a study that links DNA nanotechnology and protein engineering. The research was led by Prof. Roman Jerala from the National Institute of Chemistry and was partially conducted at our department. The authors designed stable protein–DNA composites that self-assemble into well-defined nanostructures, including nanofibers and nanorods. These hybrid assemblies not only exhibit stable morphology but also retain functional properties such as enzymatic activity and fluorescence.
The article was published in the journal Small. (https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202502060)
