Other news
Article in Physical Review E
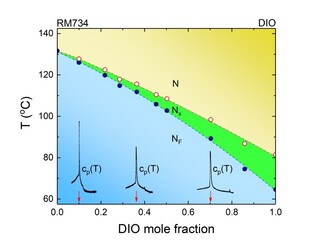
George Cordoyiannis, PhD from the Department of Condensed Matter Physics F5 and colleagues from Belgium and UK have published in Physical Review E the article Phase transitions study of the liquid crystal DIO with a ferroelectric nematic, a nematic, and an intermediate phase and of mixtures with the ferroelectric nematic compound RM734 by adiabatic scanning calorimetry.
We have studied phase transitions in a series of mixtures of liquid crystals RM734 and DIO exhibiting new types of ferroelectric nematic phases. RM734 exhibits a nematic (N) and a ferroelectric nematic (NF) phase, whereas DIO has an intermediate phase (Nx) between N and NF. By means of high-resolution calorimetry, we have derived the precise phase diagram as a function of mixture composition, i.e., as a function of variable ferroelectric coupling. The phase diagram is consistent with ideal mixture behavior, provided that the total enthalpy values are used in the analysis. The critical behavior of Nx-NF phase transition exhibited by the mixtures shows a systematic trend of the critical exponent values from α = 0.88 ± 0.10 for DIO towards α = 0.50 ± 0.05 (tricritical) when increasing the concentration of RM734.
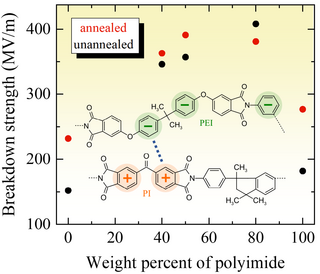
Strong enhancement of the electric breakdown strength in properly matched polymer blends
One of the major challenges in developing materials for energy storage systems is realizing high energy density while maintaining low dielectric losses. The composite approach, where conductive particles are dispersed in the dielectric matrix, effectively increases the dielectric permittivity but also boosts the losses. An alternative approach is an operation under high electric fields, i.e. increasing the electric breakdown strength (Eb) without increasing the dielectric permittivity.
Phenyl groups are fundamental chain components of many high-temperature polymers and, depending on the polymer's molecular structure, delocalized electrons in these groups may exhibit a partially positive or negative charge. We prepared blends of polyetherimide (PEI) and polyimide (PI) by the solution casting method and performed their extensive dielectric characterization. We demonstrated a significant enhancement of Eb in blends due to strong electrostatic interactions between different polymer chains; PEI namely contains three negatively charged phenyls, while PI has two strong positively charged phenyl groups. Electrostatic interactions (i) strongly reduce the number of space charges and (ii) lead to much higher chain packing density in blends. Since the breakdown is initiated by charges that are accelerated by an applied electric field in weak points, i.e. voids in the system, both features contribute to the enhancement of Eb. The blending of appropriately matched polymers thus turned out as an outstanding strategy for improving the dielectric properties of polymer systems.
Published in: Vida Jurečič, Nikola Novak, Lovro Fulanović, Vid Bobnar, Space charge contributions to the dielectric response and breakdown strength of high-temperature polyetherimide/polyimide blends, Macromolecules 56, 1097 (2023).
